deploying-elyra-in-a-jupyterhub-environment.md 3.6 KB
Deploying Elyra & JupyterHub in a Kubernetes environment
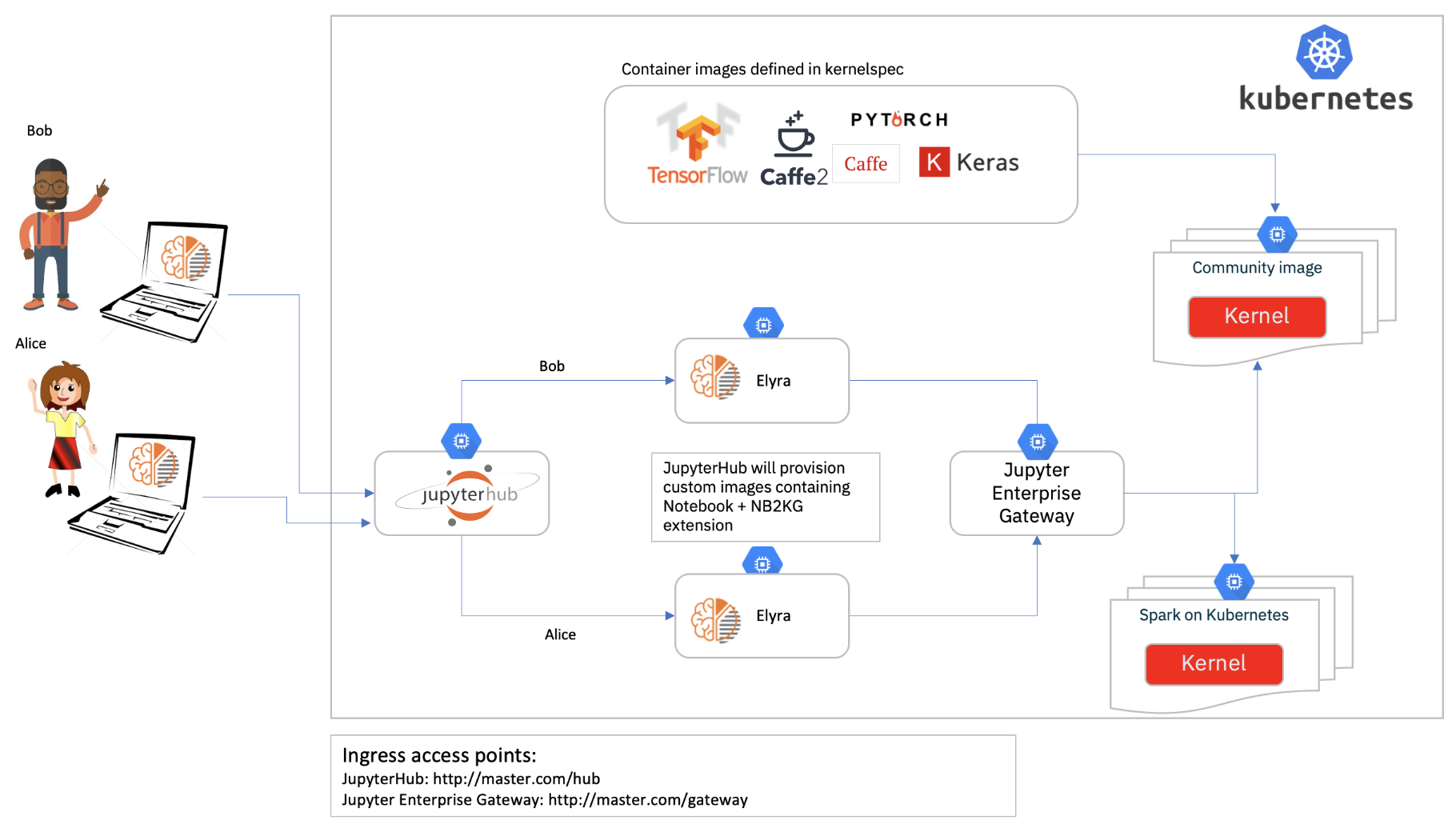
This document goes over how to integrate Elyra into a self-service Jupyter Notebook platform managed by JupyterHub in a Kubernetes environment.
The links below provide more details on how to install/configure JupyterHub:
- Zero to JupyterHub with Kubernetes
- Ansible script to deploy Elyra, JupyterHub, Jupyter Enterprise Gateway
Configuring JupyterHub Deployment
In this case, JupyterHub is the recommended entry point for Elyra, as it will manage the user authorization and provisioning of individual Notebook servers for each user.
JupyterHub is configured via a config.yaml file, and the following settings are required:
- Configure JupyterHub to use Elyra docker image when instantiating the notebook environment for each user
singleuser:
defaultUrl: "/lab"
image:
name: elyra/elyra
# change to a specific release version as appropriate
tag: dev
# disable this in a production environment
pullPolicy: "Always"
storage:
dynamic:
storageClass: nfs-dynamic
Deploying Jupyter Enterprise Gateway
Jupyter Enterprise Gateway enables support for remote kernels in a Jupyter Deployment
- Deploying Jupyter Enterprise gateway
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/jupyter/enterprise_gateway/v2.1.1/etc/kubernetes/enterprise-gateway.yaml
Connecting JupyterHub and Jupyter Enterprise Gateway
Now that all components are deployed, we need to make them aware of each other via some additional environment variables.
- Flowing current user from JupyterHub to Jupyter Enterprise Gateway
hub:
...
extraConfig: |-
from kubespawner import KubeSpawner
from tornado import gen
import yaml
class CustomKubeSpawner(KubeSpawner):
def get_env(self):
env = super().get_env()
env['KERNEL_USERNAME'] = self.user.name
return env
c.JupyterHub.spawner_class = CustomKubeSpawner
c.Spawner.start_timeout = 500
- Integrating Elyra (Jupyter Notebook) with Jupyter Enterprise Gateway
singleuser:
defaultUrl: "/lab"
image:
name: elyra/elyra
# change to a specific release version as appropriated
tag: dev
# disable this in a production environment
pullPolicy: "Always"
storage:
dynamic:
storageClass: nfs-dynamic
extraEnv:
JUPYTER_GATEWAY_URL: <FQDN of Gateway Service Endpoint>
JUPYTER_GATEWAY_REQUEST_TIMEOUT: "120"
Customizing the docker image to be used
We have created an Elyra docker image with specific dependencies required to run elyra, and that could be used to customize your environment with other additional packages required by your workloads, or any other customizations needed.
FROM elyra/elyra:dev
...